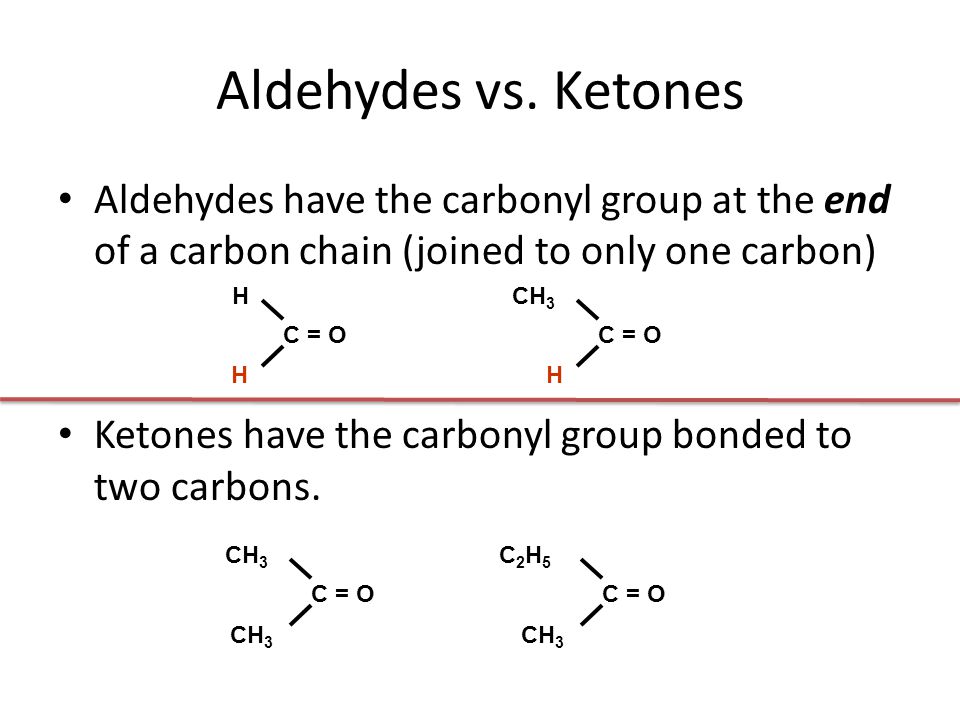
Notice that these all have exactly the same end to the molecule. All that differs is the complexity of the other group attached. When you are writing formulae for these, the aldehyde group (the carbonyl group with the hydrogen atom attached) is always written as -CHO – never as COH. That could easily be confused with an alcohol.
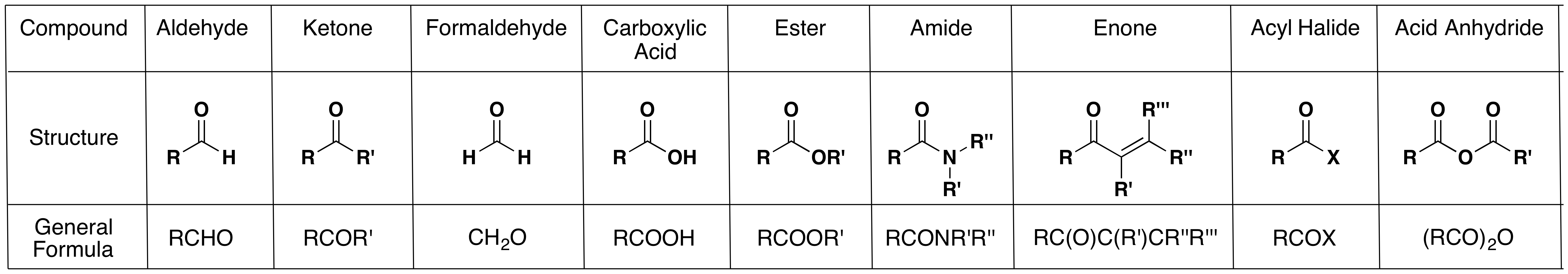

1 Overview of Carbonyl Compounds. 1. Kinds of Carbonyl Compounds. a) Aldehydes and ketones – RCOH and R 2CO.No leaving group attached to carbonyl …

Carbonyl Chemistry: Survey of Reactions and Mechanisms: When dealing with Carbonyls, we consider two general mechanism types: Carbonyls Have X as a Leaving Group Don’t have X as a Leaving Group



Aldehyde, any of a class of organic compounds, in which a carbon atom shares a double bond with an oxygen atom, a single bond with a hydrogen atom, and a single bond with another atom or group of atoms (designated R in general chemical formulas and structure diagrams). The double bond between carbon and oxygen is characteristic of all aldehydes and is known as the carbonyl group.

Chapter 19: Enols and Enolates of Carbonyl Compounds and Their Reactions We have seen that the carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones is highly reactive, and that additions to this functionality are common. In the present chapter we will see that not only is the carbonyl functionality reactive per se, but that it also activates nearby carbon …
An aldehyde / ˈ æ l d ɪ h aɪ d / or alkanal is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure −CHO, consisting of a carbonyl center (a carbon double-bonded to oxygen) with the carbon atom also bonded to hydrogen and to an R group, which is any generic alkyl or side chain. The group—without R—is the aldehyde group, also known as the formyl group.
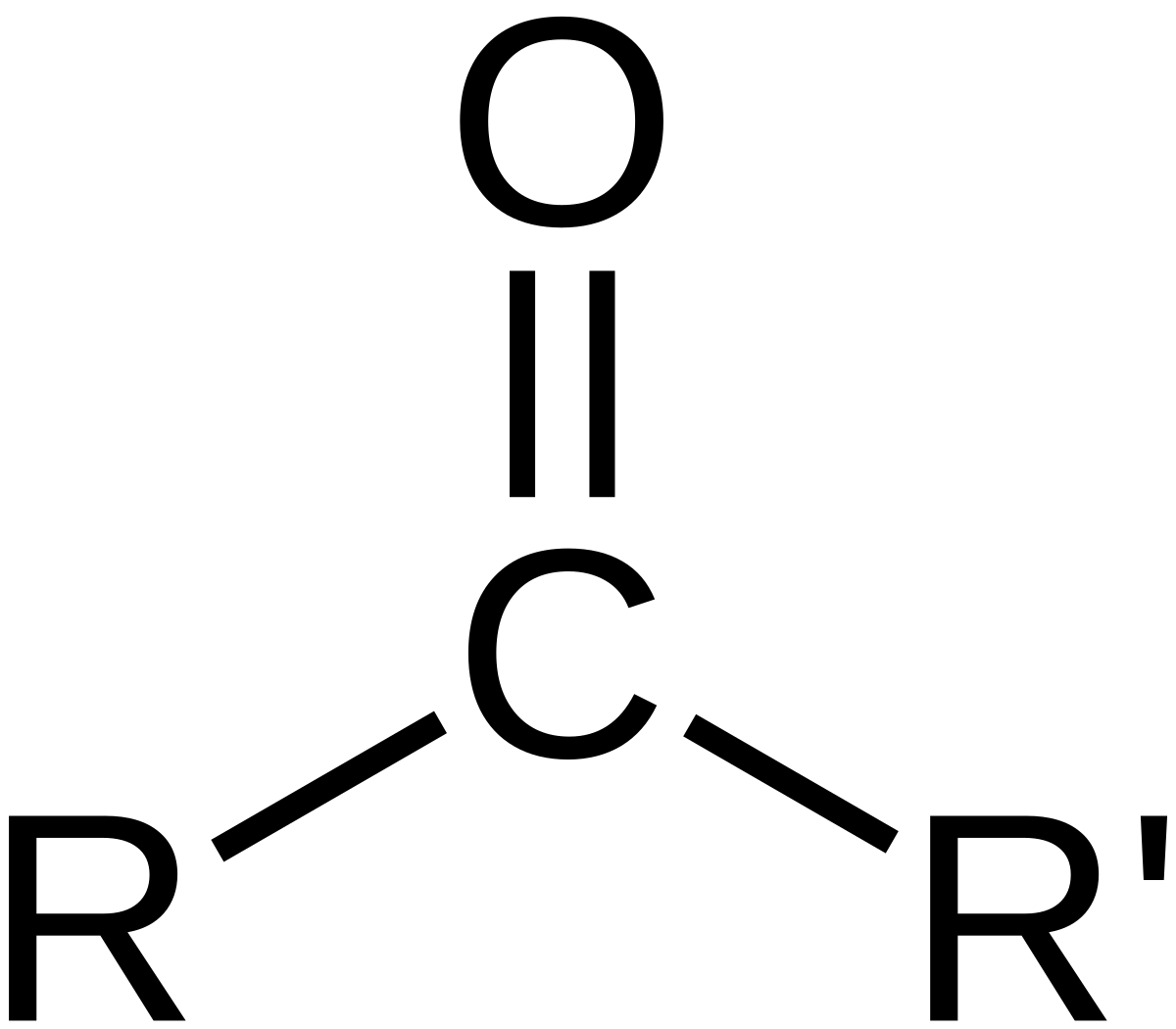
Aldehydes and Ketones 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones. Aldehydes and ketones are organic compounds which incorporate a carbonyl functional group, C=O.The carbon atom of this group has two remaining bonds that may be occupied by hydrogen or alkyl or aryl substituents.

Carbonyl Compounds – Aldehyde tests. There are a number of tests that can be used to identify the presence of a carbonyl group in a compound. These rely on the oxidising nature of the various carbonyl compounds.
Carbonyl Chemistry – Fundamentals Introduction Carbonyl group: Carbonyl functional groups: Brief Nomenclature of Aldehydes & Ketones1 IUPAC system:
Carbonyl group: Carbonyl group,, in organic chemistry, a divalent chemical unit consisting of a carbon (C) and an oxygen (O) atom connected by a double bond. The group is a constituent of carboxylic acids, esters, anhydrides, acyl halides, amides, and quinones, and it is the characteristic functional group